In an increasing virtual world, handling digital identities securely and efficiently has become a priority task for individuals and organisations. Digital identity management is not just a tag but an important aspect of our modern cyber security and users experience. In this blog, we will explore what digital identity management is , why it is important , and the best practices to implement it effectively.
Digital Identification Management (DIM) refers to the management of managing digital identity in an organization or in multiple online systems. A digital identity usually consists of usernames, passwords, biometric data and other non-public or organizational data. Digital Identity Management is important for verifying, providing access and securing statistical integrity and security.
The components of digital identity can be categorized into several key groups:
Usernames and Email Addresses: These are fundamentals for identifying one user apart from another across various platforms.
Biometric Data: Uniquely individual physical characteristics like fingerprints, facial recognition profiles, and voice profiles more and more are being employed as secure identifiers.
Passwords: Traditional method of identification confirmation, but less secure than an independent method.
Security Tokens and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add extra security by requiring extra verification methods beyond passwords.
Digital Certificates: Used by trusted parties to authenticate devices or applications to make communications secure.
Browsing and Search History: Records what one does online and assists with personalization and anomaly detection..
Purchase History: Reflects user behavior and trends in online commercial settings.
Keystroke Dynamics and Mouse Movements: Behavioral biometrics that are able to identify distinct patterns of user behavior for added security.
Personal Information: Holds the name, birth date, contact, and all static data.
Location Data: IP address or GPS-based, it can offer context to user behavior and increase security.
Social Media Connections: Social media friends, followers, and networks.
Professional Networks: Professional contacts and interactions at work places, i.e., LinkedIn.
Online Profiles and Accounts: On certain websites like social media, email, and online shopping.
Online Tracers: Identity crumbs based upon actions such as posting content, writing reviews, and browsing using browsers.
IP Address and Device Information: Helps in individualizing user experiences and enhancing security.
Cookies and Browser History: Used for user preference and tracking.
Issued by Trusted Authorities: These certificates validate devices or apps for security.
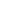
Why is digital identity management important?
Effective digital identification controllers are important for all people and agencies due to the following goals:
Enhanced security: An enhanced security describes interactions with customers, partners, applications and systems in granular detail. In short it is protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access .
User Convenience: An user convenience is the quality of something being easy to use, access, or obtain, and the ease and comfort it provides to the user, ultimately saving time and effort. Its streamlines get entry to offerings through single connected signals and MFA.
Regulatory Compliance:For its own safety and to keep itself within legally and ethically right boundaries, a business organization must be governed by all the rules, regulations, guidelines, and specifications applicable to its business processes. It adheres to information security law such as the CCPA, GDPR, and the IT Act of India.
Risk Mitigation: The activity of identifying potential risks or threats and establishing strategies to mitigate or entirely remove their impact from a project or enterprise with the long-term objective of reducing the likelihood and severity of negative outcomes.
Efficient User Management: It allows people to access resources while protecting the security and integrity of data and IT infrastructure. Eg- Automates onboarding, authentication, and access control.
It is a backbone of cutting-edge authentication (proving you're who you say you are) and authorization (figuring out what you’re allowed to do). From logging into your email to gaining access to a company VPN, DIM is everywhere.
1. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA combines a couple of authentication methods, together with passwords and biometric verification, to beautify safety.
2. Use Single Sign-On (SSO) Solutions
SSO lets users get right of entry to more than one application with a single set of credentials, improving each consumer's enjoyment and safety.
3. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encryption permits protect credentials and personal information from cyber threats.
4. Regularly Update and Monitor Access Controls
Conduct periodic audits to make certain that pleasant criminal users have the right of entry to crucial structures.
5. Educate Users on Cyber Hygiene
Train personnel and customers on exceptional practices, together with strong password advent and spotting phishing tries.
6. Leverage Biometrics for Authentication
Biometric records, together with fingerprints and iris scans, offer a better level of protection as compared to traditional strategies.
7. Adopt a Zero Trust Approach
Assume no character is depended on via default and confirm every consumer and tool having access to the network.
Human Identity: These are attributes used by human customers to access a device or agency, which embody passwords or biometric records.eg- race, ethnicity, gender, religion, nationality, and personal beliefs and experiences
Machine Identity: These are virtual credentials (e.G., IP addresses or TLS certificates) that authenticate and become aware of devices and applications within networked environments.eg- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and Robotic Process Automation (RPAs or “bots”).
Cloud Identity: An aggregate of the previous two, used to control getting admission to cloud sources.eg- Google Cloud Identity, Okta, and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
One of the most effective methods to handle and defend virtual identities is to install a strong identification and get admission to control (IAM) solution.
An IAM platform enables users to manage digital identities, furnish right of entry to, and assign user privileges based totally on particular attributes including activity name, role, location, or tool. These systems ensure that most effectively authenticated and certified customers can get right of entry to vital records and assets inside an agency.
Moreover, IAM platforms cope with the lifecycle management of digital identities. This consists of updating identities with new credentials at the same time as wished or deactivating and archiving client money owed whilst they're not required, which includes at the same time as employees leave the agency.
Despite the benefits, the weak stressful conditions are faced, including the problem of privacy and complexity of large-scale data. Decentralized identification and blockchain-based certification solutions that grow up form the future of mild. Some of future trend of IAM are:
AI-driven security : its process is powered by the capabilities of artificial intelligence. Eg- Artificial intelligence, Chatbots, ChatGPT
zero-trust architecture: it directs continuous monitoring and validation of these tools to ensure secure deployment and service delivery.
decentralized identities: it is a type of identity management that allows people to control their own digital identity without depending on a specific service provider
passwordless authentication : A process of verifying user identity without requiring passwords, instead using alternatives like biometrics, one-time passwords (OTPs), or registered devices
Leveraging advanced technology
Identity control structures regularly contain superior eras, consisting of blockchain, AI, and tool mastering, to decorate their safety and prevention capabilities.
Since a blockchain can not be hacked or altered, some corporations have superior structures that permit users to create and shop their virtual identities on a blockchain. Because a blockchain is public, customers can port this identity anywhere needed for the identification verification process.
One powerful approach to bolster virtual identification management is to limit the collection of personal records. This means amassing best the essential records required to supply offerings. For instance, if a Social Security number is not necessary, it need not be accrued. By lowering the quantity of information saved, groups not most effective lower the danger of records loss in the occasion of a breach however additionally show a dedication to respecting users' privacy.
While enforcing those high-quality practices, it's crucial to recollect the consumer experience (UX). For example, e-trade clients recognize the convenience of having their credit score card records stored for quick checkouts. Similarly, smartphone customers feel the seamless switch of apps, contacts, and possibilities whilst upgrading to a brand new tool.
Although clients and employees recognize the importance of heightened safety features, in addition they expect a clean, positive revel in across their gadgets and offerings. Therefore, locating the proper balance among sturdy safety and user-friendly design is vital.
Implementing a Secure Digital Identity Management System
E-trade platforms, SaaS applications, and other online groups can significantly advantage from a steady virtual identification control device. By integrating sturdy fraud prevention measures at each registration segment and at some point of the identification management lifecycle, agencies can efficiently combat cyberattacks aimed toward gaining access to sensitive facts, inclusive of credit card information and in my opinion identifiable records (PII).
One green manner to enhance fraud prevention is to put into effect a device intelligence tool, like Fingerprint. This tool offers browser fingerprinting, which generates a chronic tourist identifier that remains steady in the course of unique gadgets and browsers, despite the fact that the purchaser employs a VPN or incognito mode.
Strengthening Digital Identity Management with Fingerprint
Digital identities have grown to be an essential and handy technique for customers to get right of entry to gadgets, networks, and offerings. However, they also give demanding situations associated with protection, scalability, and compliance.
Adopting fine practices—which incorporates employing sturdy authentication techniques and engaging in normal audits—can drastically enhance virtual identity manipulation. However, because the complexity of virtual identities continues to grow, leveraging advanced equipment and technology will become vital for effective and scalable management.
Fingerprint, a sophisticated digital identification control answer, serves as a sturdy defense against cybercriminals trying to compromise your organisation’s data. Its Smart Signals continuously screen and come across suspicious conduct, which includes bot activity and unusual person styles, without disrupting the person reveling in it.
By integrating solutions like Fingerprint, companies can raise their virtual identity control strategies, ensuring safety without sacrificing usability.
Conclusion
Digital identity management is integral for securing on-line interactions and dealing with person access successfully. By adopting the right practices, corporations can protect touchy information while offering seamless person experiences. As digital identity maintains to adapt, staying updated with the modern day trends and technology will ensure sturdy safety and compliance.
Digital identity management is no longer a nicety—it's a necessity. Whether it's protecting online transactions, accessing healthcare, authenticating job applicants, or streamlining government processes, digital identity is at the center of trust in the digital world.
Governments, private entities, and individuals need to collaborate to implement secure and user-friendly identity management practices. This involves investing in the appropriate technology, adhering to regulatory requirements, and educating users on privacy and cybersecurity.
Going forward, the success of digital transformation efforts will be heavily dependent on how well digital identities are managed, secured, and used for innovation.
The term "digital identity management" is the processes and resources that use to protect and control data of an individual or organization's in a digital system. This includes the creation, development, maintenance, and use of digital identities.
Digital identity depends on computer-identifiable features. For example, a computer may recognize a person because they know their password or their voice at certain levels. A computer can also identify another computer using its IP address or media access control (MAC) address.
The identity and access management ensures that only the right person can access an organization's data and resources. This is a cybersecurity practice that lets IT administrators restrict access to organizational resources and allow access to only those who need it.
Digital IDs can prove a person's identity online. There are many benefits to digital IDs. It can allow a person to access online services, one of which could be bank account verification, whereas there would be no risk of harm to personal information such as a password.
Your information is private and secured through encryption. After being authenticated by a Digital ID provider, your Digital ID can be used to share only what that service requires-often your name, date of birth, and email address.
One of the most important growing trends in the decentralized identification market is the use of Self-sovereign identification (SSI) frameworks. SSI allows individuals to have, control, and share their identification data without the use of centralized middlemen.